Foreword
THE NEWMETRO PROJECT IS AIMED AT DEFINING AND SUPPORTING THE DEVELOPMENT OF SKILLED RESOURCES AND THE ENTIRE INDUSTRY 4.0 EFFORT ACROSS EUROPE, WITH A FOCUS ON TRAINING NEEDS AND EMERGING SKILLS.
The NewMetro Project will design, develop, concept-validate and experiment an innovative European shared competence framework, the related assessement and certification methods and a European Learning delivery model, based on WBL, Virtual mobility and a European set of VOOC.
Mechatronics as an emerging discipline to manage digital innovation in production systems
The NewMetro analysis  clearly demonstrates that, over the last few years, interest in mechatronics has been reinvigorated due to the advances in sensing, communication, and computing.
clearly demonstrates that, over the last few years, interest in mechatronics has been reinvigorated due to the advances in sensing, communication, and computing.
Collected data show that, nowadays, the scope of mechatronics is very vast and related to multiple fields and domains (such as the Medical field, Robotics, Automotive engineering, Mechanical, Manufacturing Industry and so on).
In addition, NewMetro’s research discovered that in the mechatronics industry, most trends focus on “less”: less power consumption, less weight, less volume and lower costs. Product competition is therefore strongly developing particularly in these areas. At the same time, the robust growth within this industry is leading to rapid growth in the number of suppliers and systems, thus creating a clear risk of substitution.
Speaking of the most important fields of technology for the Project Partner Countries, Advanced design systems and manufacturing integration is believed to be extremely relevant by Greece and Germany. On the other side, Assembly lines management in the mechanical systems industrial sector is considered crucial by Catalonia, Italy, Latvia. Among the most important areas Austria reports the Integration of manufacturing process with real time available data followed by Industrial design with advanced materials. For Poland, from the business point of view, the most important elements in the context of its Industrial Revolution are the availability of not only highly sophisticated machines, but also highly qualified employees.
The most important skills for students and entrepreneurs
Summarising entrepreneurs 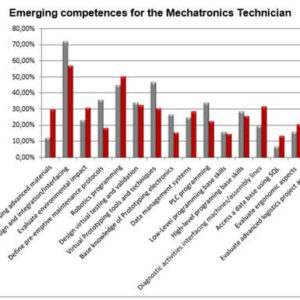 and students’ point of view, the priority competencies that a technician in mechatronic should have to comply with the production system of the future are:
and students’ point of view, the priority competencies that a technician in mechatronic should have to comply with the production system of the future are:
- System design and integration/interfacing between electronic and mechanical components, which includes the capacity to assemble and test mechatronic units, set up machine controls, customise software, adjust engineering design
- Virtual Prototyping tools and techniques (Dynamic simulations, Human in the loop simulation, HMI, AR/VR, Digital Twin development)
- Robotics programming (set up automotive robot for instance)
In general, students consider extremely relevant Aptly choosing advanced materials (especially in Catalonia, Latvia and Greece) and Robotics Programming; on the other hand, for entrepreneurs System design and Integration/Interfacing and Design virtual testing and validation has crucial importance.
Identify a European Joint Curriculum, starting from the different priorities of the partner countries
New Metro’s researches also tried to compare and classify the different priorities of the Partner Countries regarding some statements about mechatronics discipline.
tried to compare and classify the different priorities of the Partner Countries regarding some statements about mechatronics discipline.
Except for the evaluation of the statements “A mechatronics study program is an opportunity to attract new students “ and “A smart learning environment is essential for mechatronics courses “, the rest demonstrated statistically significant differences according to the respondent’s country of residence.
For example, regarding the statement Mechatronics can be considered an independent discipline Latvia was particular in favour, Italy and Greece partially agreed, whereas Catalonia expressed a contrary opinion.
The statement “To create a mechatronics study program, teachers must be retrained” have found a favourable opinion in Greece, Italy and Catalonia, whereas the statement “Learning 4.0 is very useful in mechatronics courses” is well received by all countries, albeit with less determination in Greece.
The five most important skills detected
Top 5 of the most important competencies according to all the respondents are the following:
- System design and integration/interfacing between electronic and mechanical components (assemble and test mechatronic units, set up machine controls, customise software, adjust engineering design) (Mean 0.67);
- Robotics programming (set up automotive robot) (Mean 0.43);
- Design virtual testing and validation using modelling and simulation tools (simulate mechatronic design concepts, use CAM software) (Mean 0.41);
- PLC programming (program a CNC controller) (Mean 0.40);
- Aptly choosing advanced materials that can suit product or process needs (new) (Mean 0.39).
In the identification of the most important competencies, statistically significant differences (p = 0.049) were found according to the respondent group in the evaluation of the competency PLC programming (program a CNC controller): employers consider it more important (Mean Rank 116.14) than students/young employees do (Mean Rank 100.62).
The results show that according to the employers, only Ability to work with specialised design and mechatronic machine control software is over the mean (Mean 3.03).
If you wish to get the complete scenario, take a look at the full report here.
